
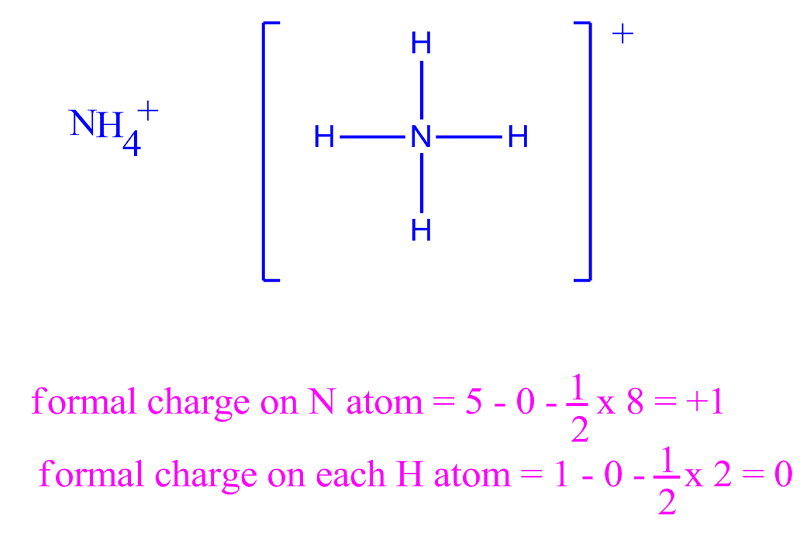
Putting these values in the above equation. Austin State University) with contributing authors. the formal charges are closest to 0 (and also the second structure does not give a complete octet on N) Contributors Paul Flowers (University of North Carolina - Pembroke), Klaus Theopold (University of Delaware) and Richard Langley (Stephen F. The bonding electrons and nonbonding electrons in the central nitrogen atom of azide are eight and zero, respectively. The first structure is the best structure. A formal charge ((FC)) compares the number of electrons around a 'neutral atom' (an atom not in a molecule) versus the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule. Calculation of formal charge for the central nitrogen atom of azide ion - The valence electrons in the N atom are five. The geometry of Molecules is a platform where we try to educate you about various chemistry concepts and find the answers you have been looking for. Determining the Formal Charge on an Atom. And it might seem challenging, but it becomes the most fun and easy subject to learn if learned the correct way. Sounds easy, right? Go ahead and try our formal charge calculator.ĭo you know that a perfect diamond is made up of a single Carbon molecule? Chemistry is one of the most exciting subjects. And to make it easy for you to do the calculations we have developed a Formal charge calculator for you, where you have to just enter the number of valence electrons, non-bonding electrons, and bonding electrons to find out the formal charge.
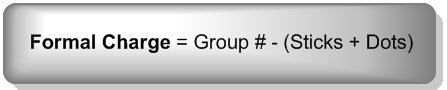
Finally, we calculate the formal charge of the oxygen. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule or ion. Similarly, you can use this formula for other molecules and find out formal charges for individual atoms in the molecule. This one has 8 bonded electrons and no unbonded, thus the FC is (5) ()(8) (0) +1. number of valence electrons for the SCl2 molecule. And using the formula stated above, we found out that the total charges on both Sulphur and Fluorine atoms are zero. Here in SF4 as all the Fluorine atoms are arranged symmetrically, they will have the same charges. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the. of valence electrons Non-bonding electrons Bonding electrons Total charge Sulphur (S) Thus, we calculate formal charge as follows: formal charge valence shell electrons (free atom) lone pair electrons 1 2 bonding electrons (3.4.1) (3.4.1) formal charge valence shell electrons (free atom) lone pair electrons 1 2 bonding electrons.
#Calculating formal charge of no how to#
Now that we know the formula let us look at the example of how to find out formal charges for individual atoms in a polyatomic molecule Let us calculate the formal charges of SF4 Atom Total no. One can calculate the formal charges for any given atom with the help of the following formula:į.C = Valence electrons – Nonbonding electrons- Bonding electrons/2 These charges help in knowing if the given structure of the molecule is stable or not. Formal charge is the individual electric charges on the atoms in a given polyatomic molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
